House in the Woods
YEAR
2013
LOCATION
Potsdam, Germany
CATEGORY
Houses
Text description provided by architect.
SMALL SPACIOUSNESS
The house in the woods is a residence for a couple and their guests.
Despite the very limited area available for construction and the users’ requirements regarding the number of beds and rooms, a residence with a perceptible spaciousness arose.
Starting from the ‘bungalow’ stereotype, the design sets openness against seclusion, introduces smooth transitions in contrast to set boundaries, emphasizes the correlation of surface and volume and, in this way, overlays the familiar with the new.
ONE SPACE RATHER THAN MANY
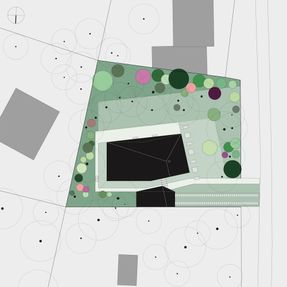
The basic structure of the compact building volume consists of two slightly rotated cuboids, each with an area of about 60 square meters.
This volumetric structure corresponds to the programmaticdivision into "living area" and "sleeping area".
Despite this functional differentiation, the open floor plan with its central bend creates a continuous, elongated space, stretching in an east-west direction, structured by an inserted wooden volume and framed by a sequence of ancillary rooms along the north.
A distance between the common and private areas of the house is achieved through the insertion of the study, guest and utility rooms.
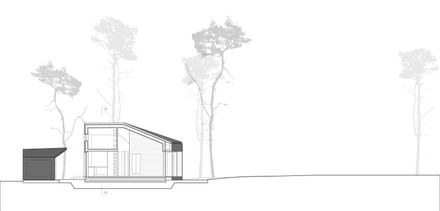
THE LARGE ROOF
The geometry of the roof is placed asymmetrically over the plan - with the ridge moved to the middle axis of the ‘living cube’ and shifted to the north.
It merges the two cuboids into oneindependent, distinct volume. The entire interior is dominated by the sloping surfaces of the roof. By means of this unifying element and the resulting height, the spaces appear generous and open.
Except for the southern facade, the roof volume traces the course of the facade. On the south side, where the outer walls meet at an obtuse angle, the roof volume stretches between the two building corners.
The resulting covered porch accentuates the building volume. Here, the plasticity of the design turns inside out and presents the inherent logic of the building.
DENSITY AND OPENNESS / TRANSITION
Along the north facade, a dense sequence of rooms, including entrance, kitchen, bathrooms and the study room with a gallery level form the functional backbone. Along the south facade the open floor plan extends to the forest and the garden.
Through the slightly angled arrangement, the spatial limits establish altering perspectives with precisely arranged windows, directing the views into the surrounding.
The large windows of the south facade emphasize the bent longitudinal axis and set the different areas of the woodland garden in relation to the interior, while the small windows of the north facade support the sculptural presence of the total volume.
They draw up vivid tableaus of the surrounding forest onto the inner surface of the northern wall.
The squared windows of the east and west facade accompany the spatial transition between the south-facing living spaces and the related areas on the north façade, sustaining the spatial continuum beyond the apparent longitudinal axis: the bedroom and the bathroom, the living room and the study room with its gallery level are tied together by the windows.
THE FOREST IN PLACE OF THE LAWN
The site is situated in a forest near Potsdam. It is distinguished by an old tree population of towering pines with their red shimmering bark as the dominant vertical elements, growing up from soft, sandy hills.
The treetop roof conjures an ever-changing play of light and shadow on the forest ground.This spectacle of light and shadow is projected onto the surfaces of the walls and the roof, while the foliage of the surrounding forest and garden is diversely reflected in the large windows.
The design enters into a dialogue with the particularities of the site. Its horizontal extent accentuates the natural, vertical elements and gives room to their wide-spreading crowns.
BLACK AND WHITE
The facade is kept in matte black. It merges modestly into the surrounding green of the forest. The white of the interior turns inside out on the southern facade, where the interior space opens towards the garden.
The interior design is discreet and forms the background for the colorful things of life.
It employs a limited range of materials and colors. Cupboards and shelves are embedded into the walls, maintaining the spaciousness of the rooms and the clarity of the overall geometry.