Ecopolis Plaza
ARCHITECTS
Ecosistema Urbano
LOCATION
Rivas-vaciamadrid, spain
CATEGORY
Other facilities
AREA
3000 m²
PHOTOGRAPHS
Emilio P. Doiztua, Mark Bentley
YEAR
2010
Text description provided by architect.
Transformation of a faceless site in Madrid’s urban sprawl, surrounded by industry and heavy traffic transportation infrastructures, into a public space for social interaction providing a building for childcare.
Contemporary society is imposing new challenges to architecture, beyond the formal experimentation that monopolizes much of its recent history.
The project “Plaza Ecopolis” aims to incorporate the idea of sustainability into daily life.
The main focus is therefore to create a vision of urban sustainability that facilitates the reduction of energy consumption by matters of design but that also aims at raising people’s awareness of their own consumption behaviour.
The layout of the building generates a public space that can be used by the area’s residents.
Another remarkable feature of the project is to consider the public space as an “open environmental classroom”, an integrated educational program for children with the goal to improve the urban environment, which among others accommodates a water purification system based on natural processes.
It is ecosistema urbano’s belief that projects as “Plaza Ecopolis” are a way to impart awareness for sustainability to children who in consequence will become responsible adults.
Resources optimization – Technologies – Economy of means: Technologies implemented at Ecopolis project are helping the initial bioclimatic design approach based on minimizing the consumption of both energy and natural resources.
Once consumption has been dramatically reduced, we analyze the use of active systems based on alternative energies.
A complete energy simulation study was developed by the Thermodynamics Research Group at the Industrial Engineering School of Seville.
This simulation study is the key to understand the behaviour of the building and it helped to select the best location for every single constructive element, adjusting the available construction budget.
An important area of the building half-buried (50% of the building takes advantage of the land’s thermal inertia) and a large glass facade facing south (700 sqm) are basic decisions that shape the physical relationship between the building and its environment.
A bioclimatic textile layer superimposed over a light steel structure is wrapping the rational concrete core of the building.
This textile (partially movable, connected with sensors to sun position) is the interface between interior and exterior spaces, blurring the boundaries between private and public and extending the inner comfort to the public space.
The Ecopolis Plaza project has the highest eco-label (A grade) of Spanish law.
The building extends its limits into the plaza and part of its functional processes are placed outside to make them more transparent to the public, creating a more conscious way of managing natural resources.
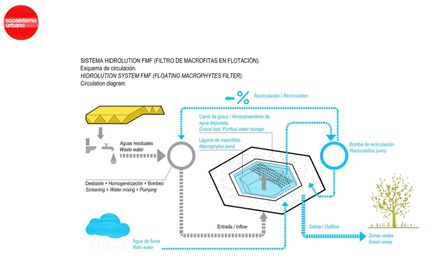
The sewage system ends into a lagoon in front of the building where all the waste water from the building is naturally purified by macrophyte plants.
All the purified water is stored under the ground within a gravel tank and it is used for all the irrigation needs of the plaza, this artificial landscape emulates a natural riverbank.
An artificial topography has been created as an enclosure and protection filter from the aggressive industrial environment, within the plaza it is easy to forget about the context and to imagine you are somewhere else, closer to nature.
Ecopolis Plaza is also a demonstrative experience of economy of means applied to the field of sustainable construction, where efficiency usually means higher construction cost.
The Ecopolis project cost per square meter is more than 35% less than a conventional building.